Aluminum Boat Trailer vs Galvanized: Which One Lasts Longer?
When choosing between aluminum and galvanized boat trailers, you should weigh corrosion resistance against strength.
Aluminum resists rust naturally, cutting maintenance and reducing weight by about half. This eases towing and boosts fuel efficiency.
Galvanized trailers offer greater tensile strength and impact durability but require periodic zinc coating upkeep, especially in saltwater.
Your decision depends on prioritizing lighter weight and corrosion resistance versus ruggedness and potential repair needs. Exploring these trade-offs will clarify the best fit for your boating demands.
- Rustproof aluminum frame
- Large 5ft. x 8ft. bed
- 1,715-lb. payload capacity
Key Takeaways
- Aluminum trailers weigh about half as much as galvanized steel, improving fuel efficiency and easing towing and maneuverability.
- Aluminum resists corrosion naturally, especially in saltwater, reducing maintenance and extending frame longevity without rust treatments.
- Galvanized trailers offer greater tensile strength and impact resistance but rely on zinc coatings that degrade over time.
- Galvanated trailers need regular inspections and zinc recoating to prevent rust, especially after saltwater exposure.
- Aluminum trailers require less corrosion maintenance but more frequent mechanical inspections and specialized repair work.
Side-by-Side Boat Trailer Comparison Table
| Feature | Aluminum Boat Trailer | Galvanized Boat Trailer |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Built from marine-grade aluminum | Constructed from steel coated with zinc |
| Corrosion Resistance | Naturally corrosion-resistant, ideal for wet conditions | Protective zinc layer, vulnerable if coating wears |
| Weight | Lightweight, easier to tow and maneuver | Heavier structure, adds towing stability |
| Structural Strength | Strong yet flexible under stress | Rigid and solid, handles heavy loads well |
| Maintenance Needs | Low maintenance, no coating to protect | Requires inspection for rust or coating damage |
| Appearance Over Time | Retains a clean, modern finish | May develop dull spots or surface corrosion |
| Environmental Exposure | Performs well in saltwater and freshwater | Better suited for freshwater use |
| Longevity Factors | Long lifespan due to oxidation resistance | Lifespan depends on zinc coating condition |
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance Requirements
Although both aluminum and galvanized boat trailers offer corrosion protection, their resistance mechanisms and maintenance demands differ markedly. Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer that effectively resists rust, even in saltwater, minimizing corrosion without additional treatments. This natural protection reduces the need for regular cleaning compared to other materials.
Aluminum and galvanized trailers protect against corrosion but differ significantly in how they resist and require maintenance.
Galvanized trailers depend on a zinc coating applied via hot-dip galvanizing, which deteriorates over time, especially under saltwater exposure, risking steel rust once compromised. This zinc coating is critical for rust prevention and requires regular upkeep to maintain its protective qualities.
You’ll need to rinse both after saltwater use to prevent galvanic corrosion, but galvanized trailers require more frequent inspections for zinc degradation, touch-ups, and occasional repainting.
Aluminum trailers avoid paint or rust treatments, reducing maintenance time and costs.
Proper care extends both trailers’ lifespan, but aluminum’s inherent corrosion resistance guarantees sustained structural integrity and lower upkeep demands, particularly in harsh marine environments. The lightweight nature of aluminum also offers advantages in fuel efficiency and ease of towing compared to the heavier galvanized steel trailers.
Weight Differences and Impact on Towing
Understanding the weight differences between aluminum and galvanized boat trailers is crucial for optimizing towing performance and vehicle compatibility.
Aluminum trailers weigh about half as much as comparable galvanized steel trailers, often saving around 1,000 pounds for tandem axle models. This significant weight reduction lowers the overall towing mass, enabling you to use vehicles with lower towing capacities and improving fuel efficiency. However, specific weight savings can vary, with some trailers showing differences closer to 200 pounds depending on design and materials. Proper maintenance and environmental exposure considerations also influence the longevity and performance of trailer materials.
You’ll also notice easier maneuverability when launching or retrieving boats due to the lighter frame. Conversely, galvanized trailers increase towing weight, demanding higher towing capacity and causing greater fuel consumption and vehicle wear.
While heavier galvanized trailers may enhance towing stability, the added mass generally imposes more strain on braking systems and drivetrain components, affecting maintenance costs. Choosing aluminum reduces these impacts, offering a more efficient towing experience.
Structural Strength and Durability Considerations
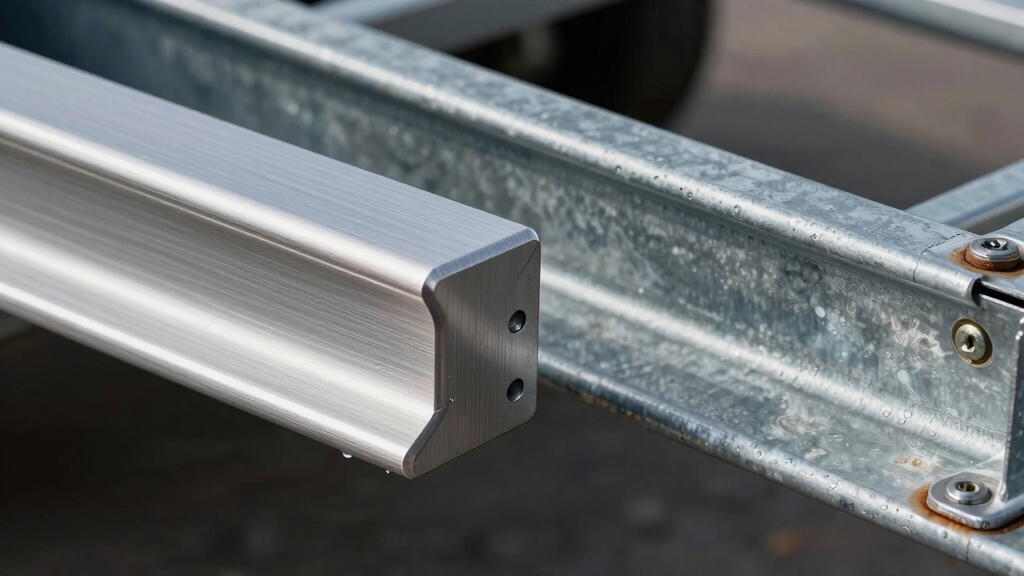

Reducing trailer weight improves towing efficiency, but you must also consider structural strength and durability to guarantee safety and longevity. Understanding the material properties is essential when making this decision.
Galvanized steel offers up to 66% greater tensile strength and superior fatigue resistance, making it better suited for heavy loads and repeated stresses. It tolerates impacts and deformation with less damage than aluminum. Additionally, steel’s higher tensile strength provides better impact and abrasion resistance compared to aluminum.
However, galvanized steel depends on zinc coatings for corrosion protection. Once compromised, structural integrity can deteriorate rapidly, especially in saltwater environments. Maintenance and protective treatments are crucial to prolonging lifespan under such conditions.
Aluminum naturally resists corrosion, preserving frame integrity over decades, though it lacks a defined fatigue limit and is more prone to superficial dents.
Marine-grade aluminum designs with I-beams can approach steel’s strength for typical boat trailers, but steel retains an edge under extreme conditions.
Your choice hinges on balancing weight benefits with structural demands and environmental exposure.
Longevity and Upkeep Costs
When it comes to trailers, you might find that aluminum ones are a lot easier to maintain. Why? Well, they’ve this great built-in corrosion resistance, which means you won’t have to worry about upkeep as often. Aluminum naturally resists corrosion and does not require paint or galvanization for protection, making it ideal for marine environments corrosion resistance. Its corrosion-resistant materials ensure long-lasting durability even in harsh conditions.
On the flip side, if you’re considering galvanized trailers, keep in mind that they rely on zinc coatings. Unfortunately, those coatings can wear down over time, especially if you’re using them in saltwater. This means you’ll likely need to inspect and repair them more frequently.
Maintenance Frequency Comparison
Aluminum and galvanized boat trailers differ markedly in maintenance frequency due to their material properties and protective coatings.
You’ll find aluminum trailers require more frequent mechanical inspections, checking fasteners, brake systems, and lubricating moving parts. They need less corrosion repair because aluminum resists rust naturally. Aluminum maintains appearance without paint but requires cleaning to prevent buildup. Regular inspection and cleaning help ensure wader durability even in harsh conditions.
After saltwater exposure, rinsing aluminum is essential to prevent salt buildup, but overall corrosion-related upkeep remains low.
Conversely, galvanized trailers demand diligent monitoring of the zinc coating’s integrity. Scratches or wear call for immediate attention to prevent steel rust.
You’ll rinse galvanized trailers regularly after saltwater use and inspect fasteners and coating condition to avoid costly corrosion damage.
Maintenance intervals for galvanized units may be longer initially but can increase as the zinc coating degrades, requiring recoating or repairs. This balances their lower upfront cost against eventual upkeep needs. The galvanized finish looks less refined but is more functional in harsh environments.
Corrosion Impact Analysis
Although both aluminum and galvanized boat trailers offer corrosion resistance, their longevity and upkeep costs differ substantially due to the distinct mechanisms protecting their materials.
Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer that shields against corrosion, enabling it to last decades with minimal maintenance. However, aluminum may corrode once deterioration starts and can be difficult or impossible to stop without specialized repair. This resilience is somewhat comparable to how neoprene waders provide durable protection in harsh conditions.
In contrast, galvanized trailers rely on a zinc coating that deteriorates, especially in saltwater, leading to rust and structural weakening over time.
Consider these factors:
- Aluminum trailers maintain structural integrity and appearance longer, resisting pitting and flaking.
- Galvanized trailers require more frequent upkeep to prevent zinc layer degradation and rust formation.
- Saltwater accelerates corrosion in galvanized trailers, markedly reducing their effective lifespan compared to aluminum.
You’ll find aluminum trailers offer superior durability and reduced corrosion-related upkeep costs in marine environments. Nonetheless, galvanized trailers can be disassembled and re-dipped to restore their protective coating, extending service life with proper maintenance.
Cost Over Time
When evaluating the cost over time for boat trailers, it’s essential to take into account both upfront investment and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Aluminum trailers demand a higher initial outlay, about $1,500 to $2,000 more than galvanized steel, but offer superior corrosion resistance and minimal upkeep. One seller claims that an aluminum trailer adds $1,500–$2,000 to the boat/trailer value, making it a worthwhile premium for many buyers. They also benefit from the ability to maintain their waterproof coatings for extended durability.
They require only routine inspections and cleaning.
Galvanized trailers, with their durable zinc coating, generally last several decades if maintained properly. However, they need periodic coating touch-ups and potential corrosion repairs, increasing long-term costs.
Additionally, aluminum’s lighter weight reduces fuel consumption and tow vehicle wear, further lowering operational expenses.
Over the trailer’s lifespan, aluminum’s maintenance savings and higher resale value often offset its premium price.
This makes it a financially sound choice for longevity and reduced upkeep compared to galvanized alternatives.
Performance in Various Boating Environments
Since different boating environments impose varying stresses on trailers, your choice between aluminum and galvanized steel markedly affects performance and longevity.
Aluminum excels in freshwater due to its natural corrosion resistance and minimal maintenance needs. Galvanized steel requires frequent upkeep to maintain its zinc coating, especially in saltwater. However, galvanized trailers offer advantages in tidal areas due to their heavier weight and reduced buoyancy, easing launch and retrieval.
For New Zealand’s coastal environment, choosing the right trailer that balances corrosion resistance and durability is crucial to protect your investment from harsh saltwater conditions. coastal environment It is important to consider the abrasion resistance of trailer materials, as this affects how well they withstand contact with rough surfaces in various environments.
Consider these key factors:
- Corrosion resistance: aluminum withstands saltwater better with marine-grade materials. Galvanized steel’s zinc layer degrades over time.
- Weight and maneuverability: aluminum is lighter, improving towing efficiency. Galvanized steel provides stability on uneven terrain, which can be essential when navigating challenging launch sites.
- Environmental impact: tidal currents favor galvanized trailers.
Freshwater ramps favor aluminum for ease of handling.
Investment Value and Cost Comparison

When looking at trailers, you’ll notice that aluminum ones generally have a higher initial price tag. This is mainly due to the costs associated with the material and the manufacturing process. On the other hand, galvanized steel trailers often come in at a more budget-friendly price right off the bat. Additionally, aluminum trailers typically feature corrosion-resistant materials, reducing long-term wear and tear.
But here’s the thing: aluminum trailers are known for their corrosion resistance. This means that while you might pay more upfront, you could save on maintenance costs down the line. That’s definitely something to think about! Additionally, the lower profile of aluminum trailers improves fuel economy when towing, which can lead to further savings over time.
Initial Purchase Price
Although aluminum boat trailers typically command a higher upfront cost due to the expense of raw materials and specialized fabrication, recent manufacturing advances have narrowed the price gap with galvanized steel trailers.
You’ll find that:
- Galvanized trailers generally range from $1,200 to $2,300, benefiting from lower steel and zinc-coating costs, which reflects manufacturing strategies focused on cost efficiency.
- Aluminum trailers often carry a premium of $1,500 to $2,000, but some models now compete closely with steel counterparts due to scaled production.
- Larger aluminum trailers cost more as heavier alloys or thicker sections are required, whereas galvanized prices scale more moderately.
When choosing, consider that while aluminum’s material and fabrication expenses raise initial costs, evolving market strategies are making aluminum trailers a viable option within competitive price brackets. Additionally, aluminum trailers offer the advantage of being significantly lighter, which can improve fuel economy and reduce wear on tow vehicles.
Long-Term Maintenance Costs
Beyond the initial purchase price, long-term maintenance costs play a significant role in determining the overall investment value of aluminum versus galvanized boat trailers.
Aluminum’s inherent corrosion resistance reduces maintenance frequency, mainly limiting upkeep to cleaning and fastener inspections, especially in saltwater environments. However, repairs can be costly due to specialized welding requirements.
Galvanized trailers demand periodic zinc re-coating and intensive fastener and electrical maintenance to prevent rust, particularly in saltwater conditions. Regular inspection is also necessary to address consumables like tires and brake pads, which commonly require attention at least annually.
Repairs are typically cheaper and simpler for galvanized trailers.
Additionally, aluminum’s lighter weight lessens tire and brake wear, indirectly lowering maintenance expenses.
In contrast, galvanized trailers’ greater mass increases such wear.
Ultimately, your choice hinges on balancing aluminum’s reduced maintenance frequency and higher repair costs against galvanized’s more frequent upkeep but lower repair expenses.
Factoring in environmental exposure and usage intensity can help optimize long-term value.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Aluminum and Galvanized Trailers Affect Boat Resale Value?
You’ll find aluminum trailers generally preserve your boat’s resale value better due to superior corrosion resistance and broader market appeal, especially in saltwater environments.
Galvanized trailers, while cheaper upfront, may depreciate faster if maintenance lapses, as corrosion undermines value.
Maintaining a galvanized trailer demands more effort to sustain resale worth.
Ultimately, choosing aluminum supports stronger long-term investment returns, attracting buyers who prioritize durability and lower upkeep.
Are There Environmental Impacts in Manufacturing Aluminum vs Galvanized Trailers?
Yes, manufacturing aluminum trailers consumes significant energy due to primary aluminum production, but using recycled aluminum cuts emissions substantially.
Galvanized steel trailers involve energy-intensive steel production plus zinc coating processes that may emit pollutants.
Aluminum’s corrosion resistance reduces chemical treatments, lowering environmental impact over time.
Although steel recycling requires more energy, its zinc coating provides corrosion protection.
Which Trailer Type Is Easier to Customize or Modify?
If you enjoy welding sparks and toxic zinc fumes, galvanized trailers are your playground.
But if you want ease, aluminum’s bolted I-beams let you bolt on parts without a welding torch or a safety hazmat suit.
Aluminum’s lighter frame simplifies handling during mods, and its corrosion resistance means less post-weld worry.
Can Either Trailer Type Accommodate Electric Braking Systems Better?
You can install electric braking systems on both trailer types effectively.
Aluminum trailers demand careful attention to brake shoe magnetism due to non-magnetic metal but offer superior corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance.
Galvanized trailers provide reliable magnetic compatibility and sturdy mounting but may suffer coating wear over time.
With proper sealed wiring and compatible controllers, both handle electric brakes well.
Your choice depends on balancing weight, durability, and maintenance preferences.
Do Aluminum or Galvanized Trailers Have Different Noise Levels While Towing?
Towing an aluminum trailer is like gliding on a calm lake compared to the galvanized’s noisier road hum.
You’ll notice aluminum’s lighter weight and torsion axles reduce vibrations and rattling.
In contrast, galvanized trailers’ heavier steel frames transmit more road noise and creaks, especially as zinc coatings wear.
Aluminum’s corrosion resistance also means less squeaking over time, while galvanized requires more maintenance to keep noise levels down during your trips.
Match Trailer Material to Long-Term Use Goals
When choosing between aluminum and galvanized boat trailers, you’ll appreciate that aluminum offers a lighter, low-maintenance option with admirable corrosion resistance, ideal for saltwater environments.
Meanwhile, galvanized trailers provide robust structural integrity and a more traditional, cost-effective solution, though they may require more attentive upkeep.
Ultimately, your decision hinges on balancing long-term investment nuances with specific towing needs and environmental exposure, ensuring you secure a trailer that aligns seamlessly with your boating lifestyle.
- Secure Tie-Downs: Elastic straps hold your boat firmly in place during transport.
- Adjustable Hitch: Variable height hitch accommodates different vehicle heights.
- Convenient Jack Stand: Fold-down trailer jack stand for easy loading and unloading.
Last update on 2026-02-22 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API